























Definition of AKI
1) Increase in Cr by greater or equal to 0.3 in 48 hours
2) Increase in Cr 1.5 x baseline within 7 days
3) UOP < 0.5 mL/kg/hr x 6 hours
Causes of elevated Cr without drop in GFR
Medications that block secretion – cimetidine, TMP, and HIV medications
Increased muscle mass
Causes of elevated BUN without drop in GFR
GIB
Albumin infusions
Steroid use
Tetracycline antibiotics
Urine sediment
Pre-renal azotemia = hyaline casts
ATN = muddy brown granular casts
AIN = sterile pyuria (+/- eosinophils)
GN = protein, dysmorphic RBCS, RBC casts
Indications for dialysis
A = acidosis
E = electrolyte abnormalities refractory to medical therapy
I = intoxicants
O = overload refractory to diuretics
U = uremia






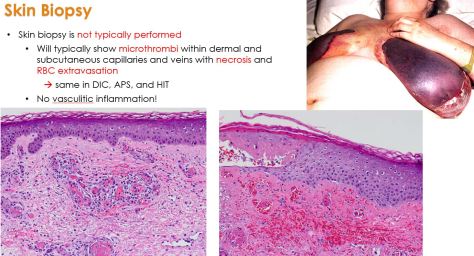

























Normal aging = no change in independent functioning
Mild cognitive impairment = stage between normal aging and dementia
Dementia = deterioration of cognitive function severe enough to impair occupational and social functioning; biggest risk factor = age
Alzheimer’s disease
Lewy Body dementia
Parkinsons dementia
Frontotemporal dementia

Standard Sizes: Beer = 12oz, Wine = 5 oz, Spirits = 1.5 oz






























Primary infection – chicken pox (lesion at varying stage on the trunk, face, and extremities)
Reactivation – shingles (painful, unilateral rash in a restricted dermatome)
Clinical manifestations – 1) Rash – most common location is thoracic and lumbar dermatomes
2) Acute neuritis – 75% of patients have pain/burning/throbbing prior to onset of rash
Complications in immunocompetent hosts – post-herpetic neuralgia (7.9%), ocular complications (1.6%),, meningitis (0.5%), oticus (0.2%)
Disseminated if > 3 contiguous dermatomes or 2 dermatomes on separate parts of the body
Diagnosis for encephalitis/meningitis – elevated WBC with lymphocytic predominance, elevated protein, positive VZV PCR or IgM
Treatment: IV acyclovir
Vaccines: Age > 60 give live vaccine unless immunosuppressed
VZIG – give to exposed pregnant or immunosuppressed patients